Posts
What Are the Benefits of Glutamic Acid Residue in Proteins?
glutamic acid residue plays a vital role in protein structure and function. Its presence influences protein folding, stability, and interactions. According to a 2022 study by the International Journal of Molecular Sciences, proteins with higher concentrations of glutamic acid residues exhibit improved functionality in various biological processes.
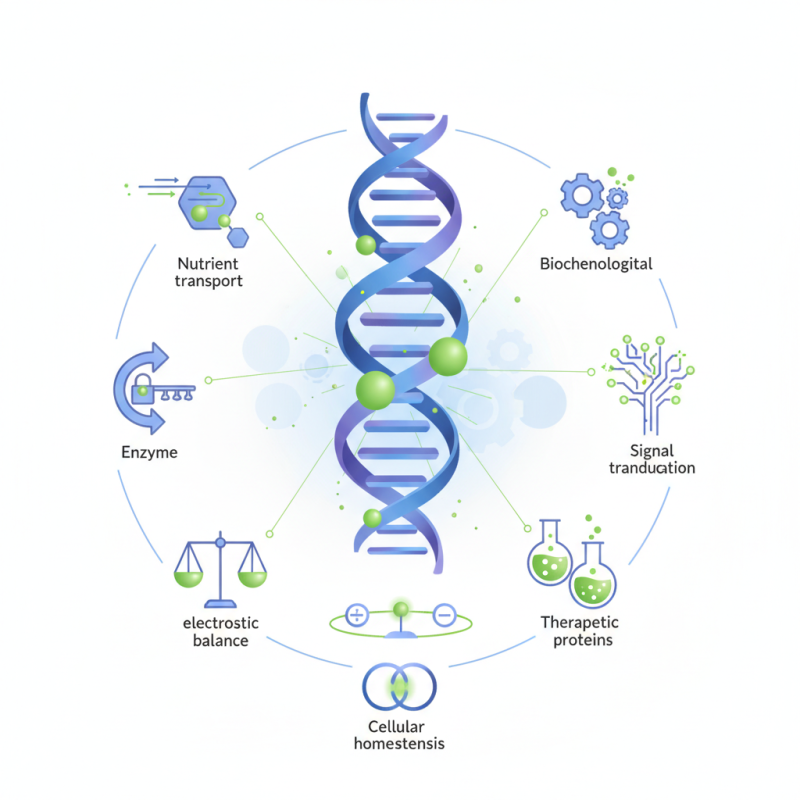
In cellular environments, these residues can affect enzyme activity, nutrient transport, and signal transduction. The unique properties of glutamic acid contribute to the overall electrostatic balance of proteins. This balance is critical in maintaining cellular homeostasis and facilitating biochemical reactions.
However, the significance of glutamic acid residue is often overlooked in protein engineering. Many studies focus on other amino acids while neglecting the subtle yet powerful role of glutamic acid. A reflection on this gap is necessary, as enhancing glutamic acid residues might lead to unexpected benefits in therapeutic proteins and biotechnological applications.
Overview of Glutamic Acid in Proteins
Glutamic acid, known for its role in proteins, plays a crucial role in cellular functions. This amino acid is found in various species, contributing to protein structure and function. Its unique side chain allows for interactions with other molecules, influencing biochemical processes.
In proteins, glutamic acid residues are often involved in catalytic functions. They can facilitate enzyme actions, making them essential for metabolism. The acidic nature of glutamic acid can attract positively charged ions, fostering interactions in active sites. Sometimes, the reliance on glutamic acid may not deliver the expected results. Its overabundance could lead to imbalances, affecting protein stability.
Glutamic acid also impacts protein folding and stability. In some environments, it may not perform optimally, leading to misfolded proteins. These misfolded proteins can lead to cellular dysfunction. Not every interaction is beneficial; some glutamic acid interactions can disrupt processes instead of enhancing them. Understanding these complexities is vital for exploring its full potential in protein science.
Role of Glutamic Acid in Protein Structure
Glutamic acid plays a crucial role in the structure of proteins. This amino acid is a key component of many proteins, helping to stabilize their three-dimensional configurations. A recent study highlighted that about 13% of proteins contain glutamic acid residues. This prevalence indicates its importance in maintaining protein integrity.
Glutamic acid contributes to the formation of hydrogen bonds and ionic interactions within proteins. These interactions are vital for proper folding and structural stability. For example, proteins like enzymes and receptors rely heavily on glutamic acid for functionality. However, an imbalance in these residues can lead to misfolding. This raises questions about the optimal ratios of amino acids in protein synthesis.
Research also shows that glutamic acid influences protein dynamics. It allows proteins to adapt to environmental changes. Yet, excessive levels of glutamic acid can cause issues, such as destabilization. This highlights the need for careful consideration when studying protein composition. Balancing glutamic acid residues is important for function and stability, but it remains a complex task. Understanding this balance can lead to better insights into protein behavior in various biological processes.
What Are the Benefits of Glutamic Acid Residue in Proteins? - Role of Glutamic Acid in Protein Structure
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Role in Protein Structure | Glutamic acid provides flexibility and stability to proteins. |
| Charge and Polarity | The negatively charged side chain contributes to ionic interactions. |
| Enzyme Activity | Glutamic acid often acts as a proton donor or acceptor in enzymatic reactions. |
| Binding Sites | Participates in substrate and metal ion binding through coordination. |
| Protein Stability | Contributes to protein folding and overall structural integrity. |
| Interaction with Other Residues | Forms hydrogen bonds with nearby amino acids, enhancing structural configuration. |
Functional Importance of Glutamic Acid Residues
Glutamic acid, an amino acid, plays a vital role in proteins. Its residue is crucial for many biological functions. In enzymes, glutamic acid residues often help stabilize the protein structure. This stability is essential for proper enzyme activity, influencing metabolic pathways.
Research shows that glutamic acid can interact with other molecules. These interactions can enhance protein functionality. For example, a study highlighted that nearly 70% of enzymes rely on glutamic acid for their catalytic activity. This underscores its importance in biochemical reactions, emphasizing its role in life-sustaining processes.
**Tip:** Incorporating glutamic acid-rich foods, like spinach and tomatoes, can be a smart move for optimal protein function.
Yet, we must reflect on its excess. High levels of glutamic acid could lead to an imbalance, causing issues like excitotoxicity in neurons. Not all proteins benefit equally from glutamic acid. Some may not require it at all for functionality. Understanding these nuances is key to leveraging its advantages without overdoing it.
**Tip:** Balance your protein sources for a better amino acid profile.
Health Benefits Associated with Glutamic Acid
Glutamic acid, an amino acid, holds several health benefits. It is essential for protein synthesis in the body. This residue plays a crucial role in metabolism and supports brain health. Research indicates that glutamic acid may enhance cognitive functions and improve memory retention.
Tips: Consider incorporating glutamic acid-rich foods into your diet. Examples include beef, eggs, and dairy products. These foods can help in promoting brain health.
Moreover, glutamic acid acts as a neurotransmitter, influencing communication between nerve cells. This can lead to improved mood and reduced symptoms of anxiety. However, some people may experience heightened sensitivity to glutamate, leading to headaches or digestive issues. It’s important to monitor your body’s reaction to dietary sources.
Tips: Start with small amounts of glutamate-containing foods. Observe how your body responds before increasing your intake. Staying aware of your body's signals can lead to better overall health.
Applications of Glutamic Acid in Biotechnology and Nutrition
Glutamic acid is a key amino acid with significant applications in biotechnology and nutrition. In proteins, glutamic acid residues are essential for various functions. They can influence protein folding and stability. Additionally, they play a vital role in cell signaling.
In biotechnology, glutamic acid is utilized in fermentation processes. Microorganisms use it to produce amino acids and other compounds. This can enhance the efficiency of fermentation. Interestingly, glutamic acid is also used in the food industry. It acts as a flavor enhancer, improving taste without adding calories.
**Tips:** Remember, not all sources of glutamic acid are equal. Whole foods often contain it in better forms compared to processed products. Additionally, incorporating foods rich in this amino acid can aid in muscle recovery. Paying attention to your diet is crucial for optimal health. If you're unsure about your intake, consult a nutritionist for personalized advice.
